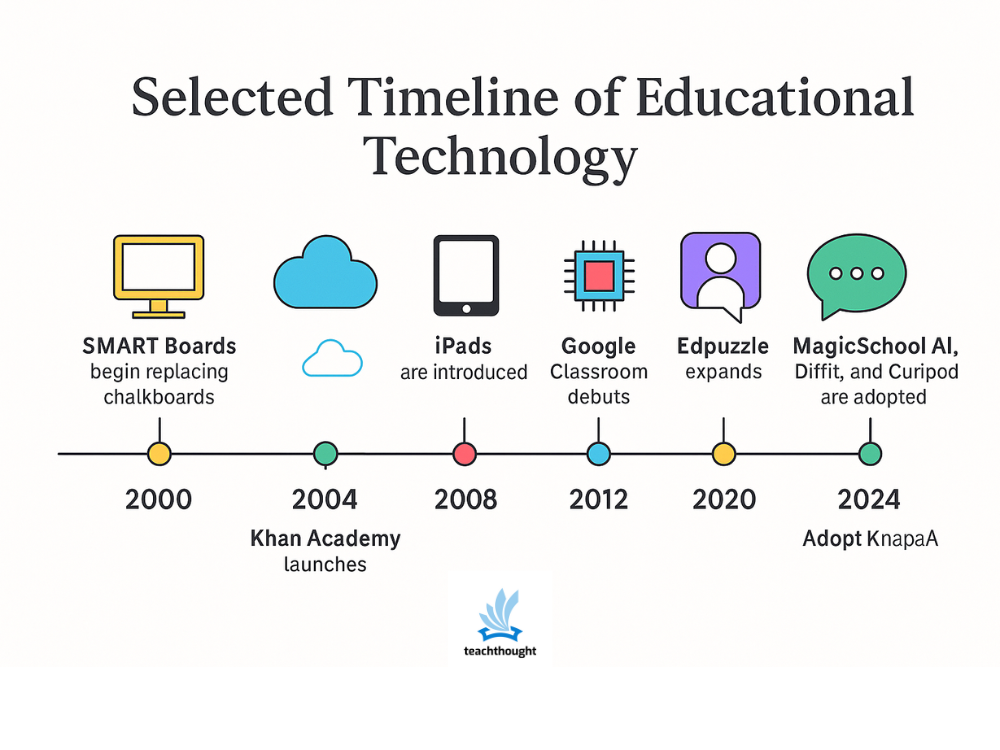
A brief history of educational technology – teaching

2000-2003
Digital tools begin to enter the classroom, led by early online platforms such as interactive whiteboards and blackboards. The shift from analog to digital teaching methods laid the foundation.
- Smart boards begin to replace blackboards in American classrooms, providing early digital interactions.
- The blackboard expands higher education, focusing on teaching syllabus, tasks and achievements.
- Brainpop and Discovery Education launches subscription-based videos and K-12 course resources.
- Microsoft PowerPoint has become a staple for teacher speeches and student projects.
2004-2007
Cloud tools and open source platforms gain momentum. YouTube and Google Docs mark a turning point in collaboration and content access.
- YouTube started and began to evolve into a major educational video content center.
- Moodle becomes a free open source LM, enabling course delivery and student tracking.
- Google Docs describe collaboration on writing tasks based on real-time browsers.
- The Maine Learning Technology Program expands one-to-one laptop program nationwide.
2008-2011
The rise of mobile devices, especially iPads, is to reshape how young learners access digital content. Khan Academy provides precedent for free, on-demand instructions.
- Khan Academy started with a brief math tutorial and became a leader in free video teaching.
- The iPad was launched in 2010 and is quickly integrated into the K-2 classroom for literacy and accessibility.
- Document camera replaces overhead projectors, allowing dynamic display and print content notes.
2012–2015
Google’s education ecosystem will be formed with classroom launch and extensive Chromebook adoption. Over the years, standards have been set for cloud-leading teaching delivery.
- Google Classroom debuted in 2014, simplifying the distribution and collection of digital assignments.
- ChromeBooks surpassed the iPad of American education for the first time, driven by cost and cloud integration.
- Nearby Pod and Pear Deck introduce interactive, device-based slideshows and polls.
2016-2019
Student voice tools, interactive videos and query-based formats gain popularity. This period is not just content access, but also focus on creation and participation.
- FlipGrid can enable asynchronous video responses for students and is becoming more and more popular in classrooms around the world.
- Edpuzzle extends the use of embedded video problems for formation evaluation.
- Adobe Spark (now Adobe Express) has become the preferred tool for students to design projects, homework, and more.
- HyperDocs became a teacher-designed Google Docs for student-based inquiry-based learning.
2020–2023
The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the full adoption of digital teaching. Teachers embrace (because what is the most choice?) asynchronous tools and enter the educational conversation.
- Remote learning during the COVID-19 pandemic has driven massive adoption of Zoom, Google Meet and Teams.
- Teachers use screen definitions and looms to record asynchronous lessons and explanations.
- Khanmigo launches as Khan Academy’s GPT-4-driven AI tutor and teacher assistant.
- Wakelet, Padlet and Jamboard (since sunset) have become popular for planning, brainstorming and visual collaboration.
2024–2025
AI tools begin to reshape teaching design, feedback and strategies. Teachers adapt to a new era of automation, moral dilemma and content generation.
- Teachers use Magicschool AI, decentralized and curators to perform scaffolding texts, distinguish tasks and quickly build materials.
- Regional implementation policies for the use of generative AI, focusing on academic integrity and authorship.
- Professional development shifts to emphasize rapid engineering, AI consistency and teaching ethics.
- Educators redesign evaluations to prioritize synthesis, real-world applications, and multi-modal expression.